Are you fascinated by the allure of the Mixolydian mode?
The Mixolydian is one of the most popular modes in music. Its distinctive sound can be found from pop to jazz and blues, making it a great choice for any singer or songwriter who wants their voice to stand out against other instruments on stage!
Whether you’re an aspiring musician or a seasoned composer, delving into the intricacies of this captivating mode can unlock a world of musical possibilities.
Join us as we embark on An Exclusive Guide of Mixolydian Mode through the depths of the Mixolydian mode and discover how to harness its unique characteristics to elevate your musical compositions.
What Is the Mixolydian Mode Used For?
The Mixolydian mode, often referred to simply as a scale, holds a prominent place in the realm of music theory. Derived from the Greek term “Mixolodi,” meaning “the song of destruction,” this mode has traversed centuries and continents, evolving into a cornerstone of various musical genres.
From its origins in ancient Greek melodies to its adaptation in modern compositions, the Mixolydian mode continues to captivate musicians and audiences alike with its distinct tonal qualities and rich historical significance.
How to Play Mixolydian Mode?
The Mixolydian mode is the fifth of all modes in music, which used to be known as Mixolodi (in Greek means “the song of destruction”). Mixolydian has its root in Mixolodi (in Greek means “the song of destruction”) and it used to be known as Mixolydishe Harmonie in Europe. In Russian folk songs, Mixolidius and Mixoliad.
1. C Major and G Mixolydian Scales
It is a more harmonically complex and less happy-sounding scale than the C Major. The major 7th interval makes all of those tones sound darker, but not as dark as they would in G or F minor scales which have 10 semitones between them instead of just 8 for this particular note pattern (aka “b7”).
2. Chords in the Mixolydian Mode
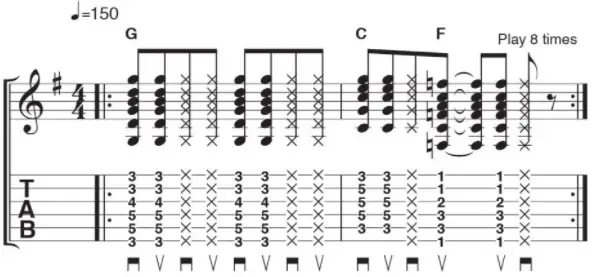
The root chord in the mode is a dominant 7th (G7 if playing G mix).
Why? The notes that make up this particular scale come from its mode: G MAJOR(A B C D E F#) takes its essential tones and creates an augmented triad with no 3rd note. If you were to take your Major Scale shape:
For example; Emaj9- Asus4…or even simpler yet would be Amin/Din seventh intervals will give birth to different sounding mode chords than just major or minor could alone – creating much more interesting harmonies than traditional ones!
3. Mixolydian Lead Lick

The Mixolydian mode is the most important and popular among solo guitarists. It can make your music sound more full, as we’ll see in this example on how to play G Mixolydian from scratch over an Am backing track:
It starts off light with just two fingers before switching up for something brighter around measure 3 or 4 when using the slide technique. At 7″ into our composition, you should already have noticed that not …”
How to Play Mixolydian Mode on Guitar?
The Mixolydian chord is major 7 (G Mixolydian would be G, A, B, C, D, E, and F#). Mixolydian chord has 1 3 5 b7. Mixolydian mode’s distinctive sound can be found from pop to jazz and blues, making it a great choice for any singer or songwriter. Mixolydian mode formula: 1 2 3 4 5 6 b7 (1 2 3 4 5 b6 b7).
Mixolydian has its root in Mixolodi (in Greek means “the song of destruction”) and it used to be known as Mixolydishe Harmonie in Europe. In Russian folk songs, Mixolidius and Mixoliad. Mixolydian mode chord: 1 3 5 b7.
Mixolydian mode chord is major 7 which has the root note is G Mixolydian would be G, A, B, C, D, E, and F#. Mixolydian chord has 1 3 5 b7. Mixolydian mode chord is major 7 which has the root note is G Mixolydian would be G, A, B, C, D, E, and F#.
Mixolydian chord has 1 3 5 b7. Mixolydian mode chord: 1 3 5 b7. Mixolydian chord is major 7 which has the root note is G Mixolydian would be G, A, B, C, D, E, and F#.
Mixolydian chord has 1 3 5 b7. Mixolydian mode chord is major 7 which has the root note is G Mixolydian would be G, A, B, C, D, E, and F#. Mixolydian chord has 1 3 5 b7. Mixolydian mode is the fifth of all modes in music, which used to be known as Mixolodi (in Greek means “the song of destruction”).
You can also check out our guide on How to Read Sheet Music for Guitar.
Frequently Ask Questions
What is the Mixolydian mode?
The Mixolydian mode stands as one of the most versatile modes in music, spanning various genres and captivating audiences with its unique tonal qualities.
What is the Mixolydian mode formula?
The Mixolydian mode adheres to a formula of 1 2 3 4 5 6 b7 (1 2 3 4 5 b6 b7), tracing its roots back to ancient Greek melodies and evolving into a cornerstone of modern music.
Conclusion: Mixolydian Mode
Armed with a comprehensive understanding of the Mixolydian mode, you are now equipped to embark on a musical journey filled with creativity and innovation.
Whether you’re composing intricate melodies, improvising soulful solos, or crafting dynamic chord progressions, the Mixolydian mode offers endless possibilities for musical expression. Embrace the richness of this timeless mode and let your creativity soar to new heights.
We hope now you can easily understand everything about Mixolydian mode. If you have any comments feel free to ask us via the comment section below.
You can also check out our guide on Types of Musical Note You Need to Use and What Are the Names of Musical Instruments.


